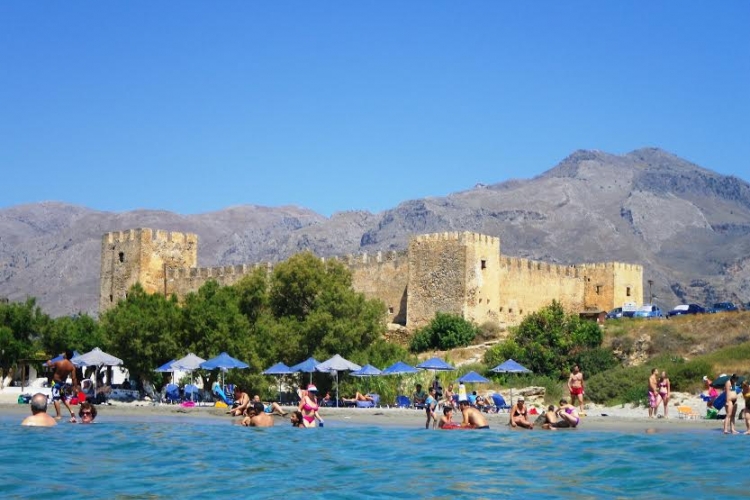
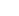Frangokastello
| Distance | 5km east of Hora Sfakion |
|---|
Only 15km east of Hora Sfakion is located the Venetian fortress of Frangokastello. The area around, appears to have already been inhabited from Paleolithic times without a break. Small stone tools, examples of caves with rocked engravings, but also Minoan ceramics were found in surface excavations (Surface Survey of American Group of Archaeologists and Scientists from 1980 entitled ‘Sfakia Mission’). Also, traces of residence seem to continue to Roman times. In the 6th Century AD a basilica was built n the foundations of which was constructed in the 13th Century the temple of Saint Nikitas, which later provided the first name for the Venetian Fort.
The Fort was constructed between 1371 and 1374, so as to exist better control of the local revolutionaries, but also as protection from the seaward side. Here, French-registered ships or vessels bound for Toulon, frequently anchored, to seek out Cretan products of well-known quality. So, from the term ‘frangos’, which for the locals described the Frenchman during the years of the Venetian and Turkish occupations, in the local dialect it, was called ‘Frangokastello’. As ‘Castel Franco’ was not given to us from Venetian sources, but they knew it as ‘Castillo di San Nikita’.
It became known for the revolution of 1821, on 18th May 1828 (and in an effort to rekindle the revolutionary movement which in Crete had weakened in 1823) here were sheltered the Greek and Cretan revolutionaries with their leader the Greek-Albanian Hatzi Michali Daliani. The movement had an ugly outcome with the death of 385 revolutionaries and the leader in a heroic exit at night and the blowing up of the fort by the Ottoman Turks. The battle which followed next, however, in retaliation for the above heroic deaths, on the part of the unruly Sfakian fighters, resulted in the slaughter and desertion of the Turkish military, with maybe 5000 victims, as extravagantly referred to in the sources from the period. The Turks would undertake the reconstruction in 1866.
This event is also connected with a natural optical phenomenon, the ‘Drosoulites’, probably a mirage; from refraction through the morning dewdrops, residents of North Africa appear like shadows of soldiers around the end of May, which many locals identify with the slaughtered revolutionaries of Daliani’s uprising.











_750_452_s.jpg)



_566_400_s.jpg)




_370_220_s_c1.jpg)



 Botanical
Botanical
 Culinary/Gastronomy
Culinary/Gastronomy
 Geology
Geology
 Hiking
Hiking
 Historical
Historical
 Village experiences
Village experiences
 Sports activities
Sports activities
 Cultural
Cultural
 Archaeology
Archaeology
 Shopping
Shopping
 Religious Tourism
Religious Tourism
 Congress
Congress
 Accessible Tours
Accessible Tours